1.) Briefly, using a diagram, choose any of the course terms/events learnt in the past modules and link them to biodiversity.
2.) Now, explain your diagram in detail (250-350 words).
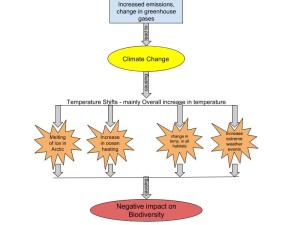
My diagram refers to Module 9- Climate change and briefly hints how it impacts the biodiversity of our world. As we learnt, increased emissions which cause change in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere lead to mostly an overall increase in temperature, which is also termed as Global Warming. The diagram explains some of the changes due to Global Warming which affect the biodiversity of our world. Firstly, it causes the Arctic sea ice to melt, which means the reflecting ice surface is replaced by dark sea water. This leads to an increased rate of heating for the sea and the air which further affect the salinity and temperatures of seawater where an entire biome resides. The species composition of the entire biome is adversely affected due to changes in their habitat. Secondly, climate change increases the ocean heating rate all over the Earth and increased level of CO2 emissions in the air also increase CO2 in the ocean which lead to ocean acidification. The temperature change along with the chemical change (ocean acidification) of seawater affect the plants and animals living in the habitat. While temperature leads to changes in species composition as certain species adapt to certain temperatures, chemical change affects the abilities of the plants and animals in various processes. Thirdly, temperature changes affect other natural habitats such as mountains, forests, grasslands, deserts and tundra regions. Temperature shifts across the Earth alter the temperatures over these habitats. This leads to change in the habitat conditions, affecting the abilities of the plant and animal species in those areas to adapt. Fourthly, temperature shifts also lead to increase in extreme weather events such as flooding and draughts due to change in patterns of rainfall and melting of mountain glaciers. These then lead to significant impact on biodiversities of the areas affected by such events. Overall, we learn how food chains, species composition, adaptation and resources including water and medicinal from the flora and fauna are affected, leading us to believe that biodiversity of all the above mentioned areas is threatened by climate change in various ways.
3.) Lastly, identify threats to biodiversity in your hometown it has or had in the past. give suggestions on how to prevent them or explain how they were overcome? (150-250 words)
My hometown Jaipur is the capital of the desert state of Rajasthan in the western part of India. Being a desert state, about two-thirds of the state is desert and one third is plain land with approximately 9% forest cover. Hence, biodiversity plays an important role in the state’s existence. One of the most major threats to the biodiversity is increasing population. We observe from the map given in the module-10, that the state is overly populated. Increasing population leads to people clearing even more land for other purposes causing an irreversible damage to the biodiversity of the state, hence habitat loss is another threat the state faces. Apart from this, the temperature shifts are affecting the state’s habitat as well, affecting the abilities of the existing species to adapt. All these issues highlight the importance of addressing them right away as further delay would lead to further irreversible damage, harming the state’s biodiversity extensively and increase ecological pressure on the state. In my opinion, being residents of the state, it is equally our duty as much as it is the state’s government’s. Together we should adopt more sustainable ways such as using barren land and putting it into use rather than destroying usable habitats, raising awareness and educating people about the topic by campaigns and workshops, protecting all the species of plants and animals in the area, in order to protect the biodiversity of the state. The government should implement rules for such protection and the public should corporate with government and follow the rules. The state’s biodiversity board can also adopt ways to preserve and increase the biodiversity by planting more seeds of the same species and of different non-invasive species along with protection of the fauna in the state, in order to allow them to increase to beneficial number as well.

Hey there Akiksha! My name is Katy. I really like you diagram. I like that you diagram ties other modules from the class into this one. Also, I like that you used different colors and shapes. This made the diagram very easy to understand. Our post are both about the same module but our questions are very different. You can view my post here https://wp.me/p3RCAy-eRC.
Hello Akiksha, my name is Rachael, I was very interested by your Learning Activity. I liked how you brought information from past modules and interconnected it with the topic of biodiversity. You’re diagram was very well set-up and explained in great detail. For your last question, I asked a very similar question and was very intrigued by the difference of our answers. India has very different biodiversity than my hometown and even most states in Northern United State. Overall, great job! If you’d like to check out my blog the link is http://sites.psu.edu/geog30/2016/04/13/module-10-biodiv…rachael-donnelly/
Hi Akiksha, great post. I like how you showed very simply all the effects that could result from climate change in your diagram. A lot of people don’t know what the actual results are, so it is good to have this easy to read information. I also found it very interesting how you included stuff about your hometown. It is always fun to read what other people’s experiences were like at home, especially when it is a whole different country. If you want to check out my post, go to: http://geog030.dutton.psu.edu/2016/04/14/module-10-3/